NAT testing, or nucleic acid testing, has become a pivotal method in blood screening to enhance the safety of blood transfusions. This advanced molecular technology is designed to detect viral nucleic acids, significantly reducing the risk of transfusion-transmitted infections in recipients. Sansure is at the forefront of providing reliable NAT testing solutions that contribute to safer blood donation practices.
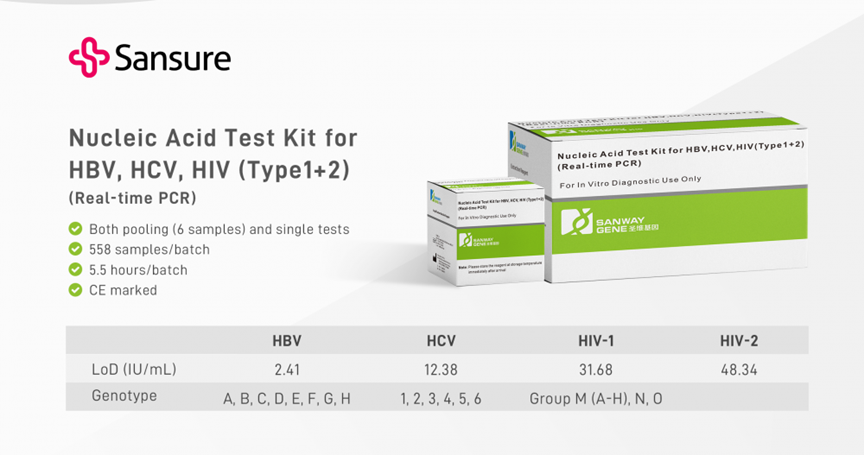
The Importance of NAT Testing
NAT testing of blood was introduced in developed countries in the late 1990s and early 2000s, with approximately 33 countries now implementing NAT for HIV and around 27 countries for Hepatitis B Virus (HBV). This technology is highly sensitive and specific, allowing for the detection of viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) at very early stages of infection. By identifying infections sooner than traditional screening methods, NAT testing significantly shortens the window period for HIV, HBV, and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infections.
How NAT Testing Works
The process of NAT testing involves amplifying target regions of viral nucleic acids, which enables the detection of even the smallest quantities of viral material in a blood sample. This high level of sensitivity makes NAT testing an essential tool in ensuring the safety of blood donations. By employing this technology, healthcare providers can identify potentially infectious blood and prevent it from being transfused into patients.
The Future of NAT Testing in Blood Screening
The automation of blood donation screening has been nearly fully realized since the introduction of NAT testing. This advancement has reduced the residual risk of transfusion-transmitted infections to almost zero. NAT testing has reached remarkable precision, capable of detecting just one molecule of DNA or RNA in a reaction tube. Future developments in this area may include increased multiplexing capabilities, allowing for the simultaneous detection of multiple viruses, and enhanced laboratory automation.
For large blood centers handling thousands of samples daily, these advancements will streamline operations and improve efficiency. Additionally, smaller benchtop devices with high flexibility and a broad detection range will be beneficial for small to medium-sized blood banks focused on patient diagnosis and blood donor screening.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding what is NAT testing of blood is crucial for appreciating its role in modern transfusion medicine. By utilizing nucleic acid testing, healthcare providers can significantly enhance the safety of blood donations and transfusions. Sansure is committed to advancing NAT technology, ensuring that blood screening remains as effective and reliable as possible. As the field continues to evolve, NAT testing will play an increasingly vital role in protecting patients from transfusion-transmitted infections, paving the way for safer healthcare practices.